TPWG315 380 DIGITAL PRESSURE GAUGE
Brief
Along with the property of PE material continuous perfecting and raising, PE pipe are extensively used in gas and water supply, sewage disposal, chemical industry, mine and so on.
Our factory has been researching and developing TPW series plastics pipe butt fusion machine that is suit for PE, PP, and PVDF more than ten years.
Today, our products include eight kinds and over than 20 types which apply to plastics pipe construction and make fittings in workshop as follows:
| SHS series socket welder | TPWC series Band saw |
| TPW series manual butt fusion machine | TPWG series workshop welding machine |
| TPWY series butt fusion machine | Series special tools |
| QZD series Auto-butt fusion machine | SHM series saddle fusion machine |
This manual is for TPWG315 plastic pipe workshop welding machine. In order to avoid any kind of accident caused by electrical or mechanical. It’s suggested to read carefully and follow the following safety rules before operating the machine.
Special Description
Before operating the machine, anyone must read this description carefully and keep it well to ensure the equipment and operator’s safety, as well as others’ safety.
2.1 The machine is used to weld pipes made from PE, PP, PVDF and can not be used to weld material without description, otherwise the machine may be damaged or some accident may be resulted in.
2.2 Don’t use the machine in a place with potential hazard of explosion
2.3 The machine should be operated by responsible, qualified and trained personnel.
2.4 The machine should be operated on a dry area. The protective measures should be adopted when it is used in rain or on wet ground.
2.5 The machine required 380V±10%, 50 Hz power supply. If extend cable should be used, there should be enough section according to their length.
Safety
3.1 safety marks
The following marks are fixed to the machine:
3.2 Precautions for Safety
Take care when operating and transporting the machine according to all the safety rules in this instruction.
3.2.1 Notice when using
l The operator should be responsible and trained personnel.
l Completely inspect and maintain the machine per year for the safety and machine’s
reliability.
3.2.2 Power
The electricity distribution box should have ground fault interrupter with relevant electricity safety standard. All safety protection devices are indicated by easily understandable words or marks.
3.2.3 Turn power off before removing the safety cover or net.
Connection of machine to power
The cable connecting machine to power should be mechanical concussion and chemical corrosion proof. If the extended wire is used, it must have enough lead section according to its length.
Earthing: The whole site should share the same ground wire and the ground connection system should be completed and tested by professional people.
3.2.3 Storage of electrical equipment
For the min. dangers, all equipment must be used and stored correctly as follows:
※Avoid using temporary wire not complying with standard
※ Do not touch electrophorus parts
※ Forbid hauling off the cable to disconnect
※ Forbid hauling cables for lifting equipment
※ Do not put heavy or sharp object on the cables, and control the temperature of cable within limiting temperature (70℃)
※ Do not work in the wet environment. Check if the groove and shoes is dry.
※ Do not splash the machine
3.2.4 Check insulation condition of machine periodically
※ Check the insulation of cables specially the points extruded
※ Do not operate the machine under extreme condition.
※ Check if the leakage switch works well at least per week.
※ Check the earthing of the machine by qualified personnel
3.2.5 Clean and check the machine carefully
※Do not use materials (like abrasive, and other solvents) damaging the insulation easily when cleaning the machine.
※ Make sure the power is disconnected when finishing job.
※Make sure there is no any damage in the machine before reusing.
If only following above mentioned, the precaution can work well.
3.2.6 Starting
Make sure if the switch of the machine is closed before powering it on.
3.2.7 Tightness of parts
Make sure the pipes are fixed correctly. Ensure that it can move well and prevent it from sliding down.
3.2.8 Working environment
Avoid using the machine in the environment full of paint, gas, smoke and deoil, since the infection of eyes and respiratory tract would be caused.
Do not put the machine in a dirty place.
3.2.9 Personnel safety while working
Remove jewelry and rings, and does not wear loose-fitting clothing avoid wearing shoe lace, long mustache or long hair that may be hooked into the machine
3.3 Equipment Safety
Hydraulic workshop welding machine is only operated by a professional or worker with trained certificate. A layman may damage the machine or others nearby.
3.3.1 Heating plate
l The surface temperature of the heating plate could reach 270℃.Never touch it directly to avoid getting burnt
l Before and after using, clean the surface with a soft cloth. Avoid abrasive materials that may damage the coating.
l Check the heating plate cable and verify the surface temperature.
3.3.2 Planing tool
l Before shaving the pipes, ends of pipes should be cleaned, especially clean the sand or other draff crowed around the ends. By doing this, the lifetime of edge can be prolonged, and also prevent the shavings are thrown out to danger people.
l Assure planing tool is lock tightly by the two pipe ends
3.3.3 Mainframe:
l Make sure the pipes or fittings are fixed correctly to get the right alignment.
l When joining pipes, the operator should keep a certain space to the machine for personnel safety.
l Before transporting, make sure all the clamps are fixed well and can not fall down during transportation.
Applicable Range And Technical Parameters
| Type |
TPWG315 |
|
| Materials for welding |
PE,PP ,PVDF |
|
| Outside Diameter
ranges |
elbow (DN,mm) |
90 110 125 140 160 180 200 225 250 280 315mm |
| tee (DN,mm) |
90 110 125 140 160 180 200 225 250 280 315mm |
|
| cross (DN,mm) |
90 110 125 140 160 180 200 225 250 280 315mm |
|
| Wyes 45°& 60° (DN,mm) |
90 110 125 140 160 180 200 225 250 280 315mm |
|
| Environment temperature |
-5~45℃ |
|
| Hydraulic oil |
40~50(kinematic viscosity)mm2/s, 40℃) |
|
| Power supply |
~380 V±10 % |
|
| Frequency |
50 Hz |
|
| Total current |
13 A |
|
| Total power |
7.4 KW |
|
| Include, heating plate |
5.15 KW |
|
| Planing tool motor |
1.5 KW |
|
| Hydraulic unit motor |
0.75 KW |
|
| Insulating resistance |
>1MΩ |
|
| Max. hydraulic pressure |
6 MPa |
|
| Total section of cylinders |
12.56 cm2 |
|
| Max. temperature of heating plate |
270℃ |
|
| Difference in surface temperature of heating plate |
± 7℃ |
|
| Undesired sound |
<70 dB |
|
| Oil tank Volume |
55L |
|
| Total weight(kg) |
995 |
|
Descriptions
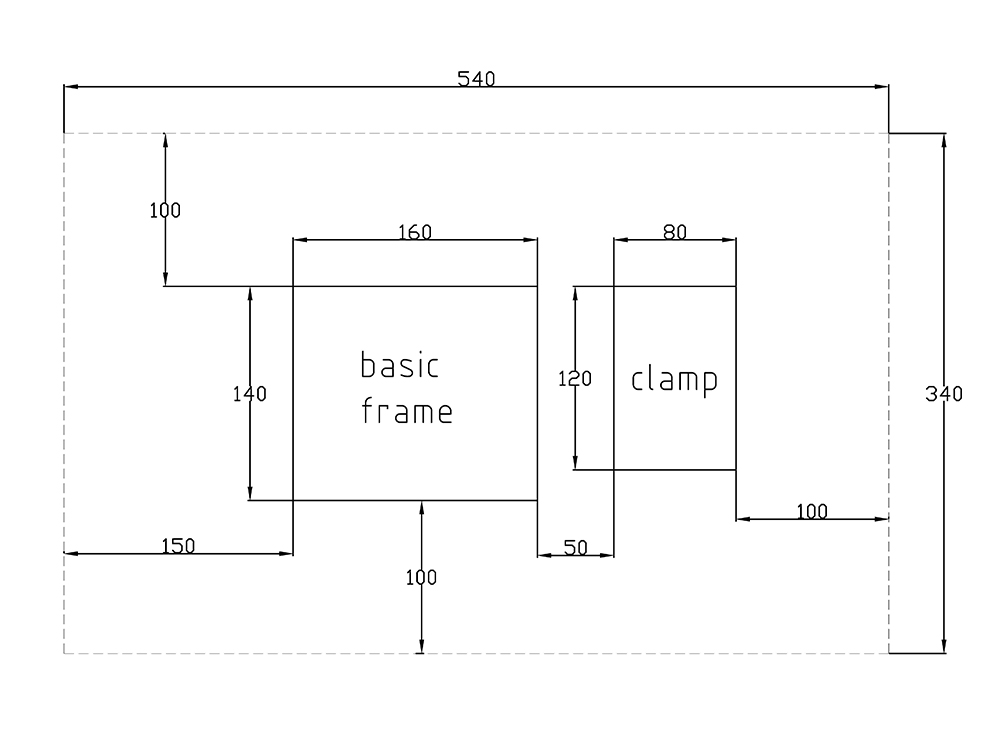
The workshop welding machine can produce the elbow, tee, cross by PE pipe at workshop. The standard clamps conform to the standard pipes’ sizes according with ISO161/1.
5.1 Main machine
|
1. Planning tool |
2. Heating plate |
3. Operation panel |
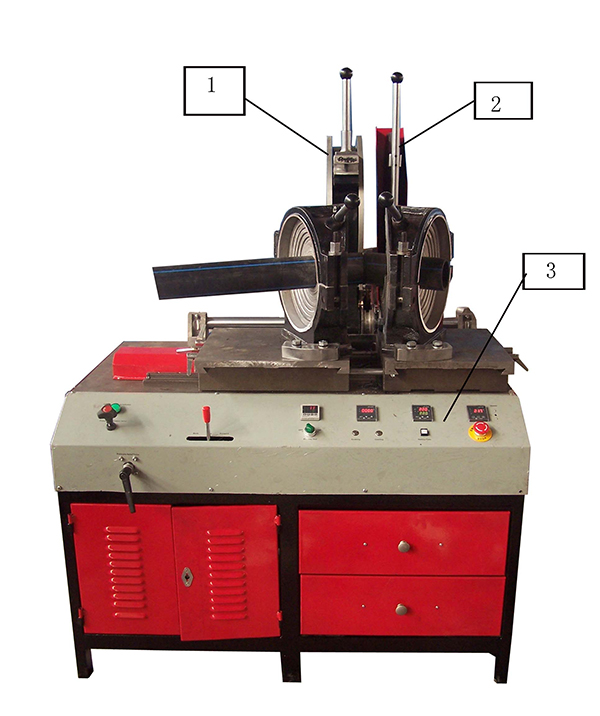
5.2 Operation panel
| 1. Pressure Regulation Valve | 2. Pressure Relief Valve | 3. Oil Pump Working Indicator | 4. Direction Valve |
| 5. Digital Pressure Meter | 6. Planing Button | 7. Timer | 8. Soaking Time Button |
| 9. Temperature Control Meter | 10. Cooling Time Button | 11. Voltmeter | 12. Heating Switch |
| 13. Emergency Stop | 14. Buzzer |
Installation
6.1 Lifting and installation
When lifting and installing the machine should be kept it horizontal, and never incline or reverse it to avoid unwanted damage.
6.1.1 If a forklift is used, it should be inserted carefully from the bottom of the machine carefully to avoid damaging the oil hose and circuit
6.1.2 When conveying the machine to installation position, the mainframe should be kept stable and horizontal.
6.1.3 Install the motor to the reduction box of the planing tool and fixed by screws, shown in Fig .3.

6.2 Connection
Make sure that the space is enough for putting the machine and keep the whole machine horizontal and assure the correct connection of all sockets, cables and hoses when installing the machine.
6.2.1 Connect the main machine to electrical box.


Fig. 4 Connect heating plate to electrical box
Fig. 5 Connect planning tool to electrical box
6.2.2 Connecting the cable of the machine to power, which is three phases- five wires 380V 50HZ.
For safety, the machine must be earthed from ground point of the machine.
6.2.3 Fill the filtered hydraulic oil. The height of the oil should be more 2/3 of the height of the scope of content gauge.
Warning: Earthing must be finished by professional people.
Instruction For Use
Follow all the safety rules on the machine. Untrained person is not allowed to operate the machine.
7.1 Power
Close the ground fault interrupter
7.2 Start oil pump
Start the oil pump to watch the rotating direction. If the pressure gauge has readings, the rotation is right, if not, exchange any two live wires.
7.3 Check and adjust drag pressure and move speed of drag plate. Working pressure of the system is 6 MPa. The joining pressure can be adjusted by pressure regulation valve located on the control panel. The planing pressure should be increased gradually, and keep it when continuous shavings appear (not too big). Feed speed of drag plate can be adjusted through the check valve (inside the base).
7.4 Clamps Installation
Install left and right clamp seats (clamps for tees or elbows) according to fittings to be fabricated.
1) Fix them firstly by the lock pin attached with the machine;
2) Adjust the angle with the special location handle;
3) Tighten the lock screw with a wrench.
If the elbow clamps needed to be used, press them tightly with the lock plate after adjust the angle.
7.5 Set specified temperature on temperature controller according to pipe welding process. (See section 7.10)
7.6 Before raise or lower the planing tool open the lock device on the handle.
7.7 Pipes positioning into the machine
7.7.1 Separate the clamps of the machine by acting on lever of direction valve
7.7.2 Position the pipes into the clamps and fasten them; the space between two pipe ends should be enough for planing tool.
7.7.3 Lock pressure relief valve, while close the two ends, turn the pressure regulation valve till the pressure gauge indicates fusion pressure, which is determined by the pipe materials.
7.8 Planing
7.8.1 Separate the clamps by acting on direction valve and fully open pressure relief valve.
7.8.2 Place the planing tool between the two pipes ends and switch on, approach the pipes ends towards the planning tool by acting on direction valve “forward”, and adjust the pressure regulating valve to keep suitable pressure till continuous shavings appear from the two sides.Note: 1) Thickness of the shavings should be within 0.2~0.5mm and it can be changed by adjusting the height of the planing tool.
2) Planing pressure should not exceed 2.0 MPa to avoid the damage of the planning tool.
7.8.3 After planing, Separate the clamps and remove planning tool.
7.8.4 Close the two ends to align them. If the misalignment exceeds 10% of the pipe thickness, improve it by loosening or tightening the upper clamps. If the gap between the ends exceeds10% of the pipe’s wall thickness, planing the pipe again till get the requirement.
7.9 Welding
7.9.1 Set the soaking time and cooling time according to the welding process.
7.9.2 After removing planing tool, place heating plate, Lock gradually pressure relief valve while pushing forward direction valve, which increases heating pressure to the specified fusion pressure(P1). The pipe ends stick to heating plate and the fusion begins.
7.9.3 When a small bead build up, push back the direction valve on the middle to keep the pressure. Turn swing check valve to lower the pressure to soaking pressure(P2) and then lock it quickly. Then push down the soaking time button to time.
7.9.4 After the soaking (the buzzer alarms), open the clamps by acting on the direction valve and remove heating plate quickly.
7.9.5 Join the two melted ends quickly and keep the direction valve on the “forward” for a short time and then push back to the middle position to keep pressure. At this time, readings in pressure gauge is the set fusion pressure (if not, adjust it by acting on pressure regulation valve).
7.9.6 Push down the cooling time button when cooling begins. After the cooling time elapses, the buzzer alarms. Relive the system pressure by acting on pressure relief valve, open the clamps and remove the joints.
7.9.7 Check the joint according to welding process standards.
7.10 Temperature controller and timer
7.10.1 Timer setting
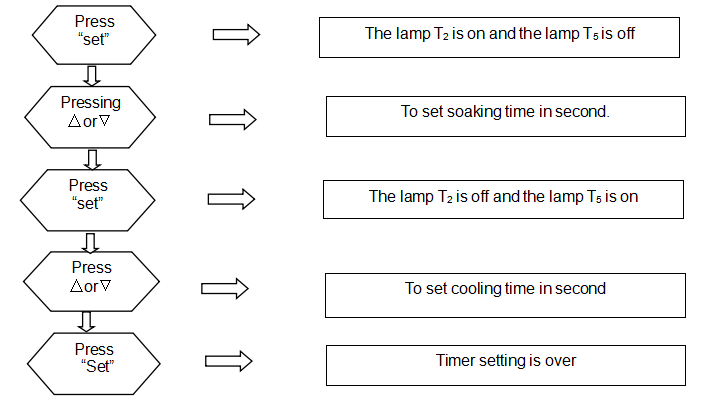
7.10 Temperature controller and timer
7.10.1 Timer setting
7.10.2 Timer using
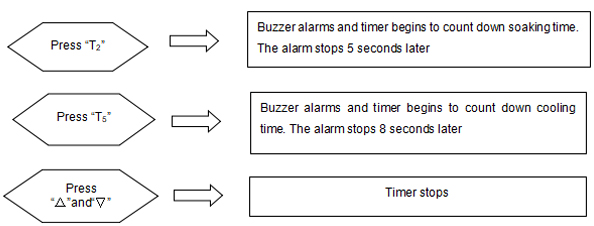
7.10.3 Temperature controller setting
1) Press “SET” for more than 3 seconds till “sd” is shown in the upper window
2) Press “∧” or “∨” to change the value to specified temperature (press“∧” or “∨” continuously, the value will plus or minus automatically)
3) After setting, press “SET” to go back to monitoring and controlling interface
Reference Welding Standard(DVS2207-1-1995)
8.1Because of different welding standards and PE materials, the time and pressure of phase of fusion process are different. It suggests that t he actual welding parameters should be proved by pipes and fittings manufactures
8.2 Given welding temperature of pipes made from PE、PP and PVDF by DVS standard ranges from180℃ to 270℃. Application temperature of heating plate is within 180~230℃, and its Max. surface temperature can reach 270℃.
8.3 Reference standard DVS2207-1-1995
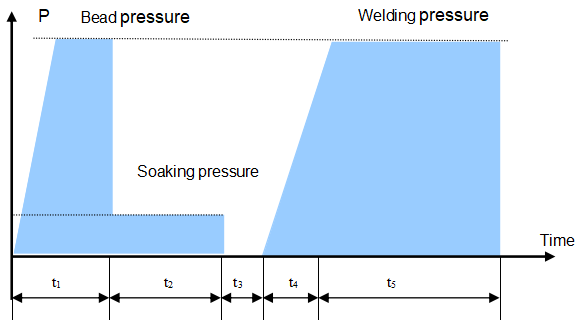
|
Wall thickness (mm) |
Bead height(mm) |
Bead build-up pressure(MPa) |
Soaking time t2(Sec) |
Soaking pressure (MPa) |
Change-over time t3(sec) |
Pressure build -up time t4(sec) |
Welding pressure(MPa) |
Cooling time t5(min) |
|
0~4.5 |
0.5 |
0.15 |
45 |
≤0.02 |
5 |
5 |
0.15±0.01 |
6 |
|
4.5~7 |
1.0 |
0.15 |
45~70 |
≤0.02 |
5~6 |
5~6 |
0.15±0.01 |
6~10 |
|
7~12 |
1.5 |
0.15 |
70~120 |
≤0.02 |
6~8 |
6~8 |
0.15±0.01 |
10~16 |
|
12~19 |
2.0 |
0.15 |
120~190 |
≤0.02 |
8~10 |
8~11 |
0.15±0.01 |
16~24 |
|
19~26 |
2.5 |
0.15 |
190~260 |
≤0.02 |
10~12 |
11~14 |
0.15±0.01 |
24~32 |
|
26~37 |
3.0 |
0.15 |
260~370 |
≤0.02 |
12~16 |
14~19 |
0.15±0.01 |
32~45 |
|
37~50 |
3.5 |
0.15 |
370~500 |
≤0.02 |
16~20 |
19~25 |
0.15±0.01 |
45~60 |
|
50~70 |
4.0 |
0.15 |
500~700 |
≤0.02 |
20~25 |
25~35 |
0.15±0.01 |
60~80 |
Remark:Bead build-up pressure and welding pressure in the form is the recommended interface pressure, the gauge pressure should be calculated with the following formula.

The Procedure For Fitting Fabricating
9.1 Elbow making
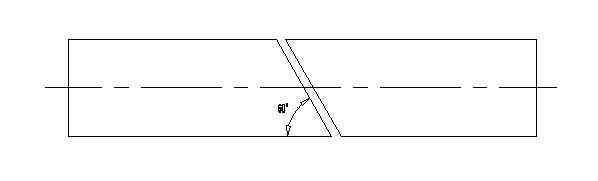
9.1.1 According to the elbow’s angle and quantity of welding parts, the welding angle between every part can be decided.
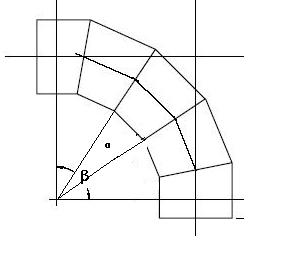
Explanation: α - welding angle
β - elbow angle
n - quantity of segments
For example: 90°elbow is divided into five segments to be welded, the welding angle α=β/(n-1)=90°/(5-1)=22.5°
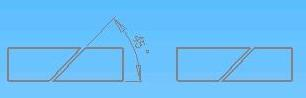
9.1.2 The min dimension of every welding part in the welding parts quantities is cut by the band saw according to the angle.
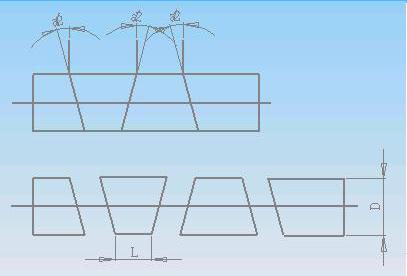
Explanation:
D - outside diameter of the pipe
L - Min length of every part
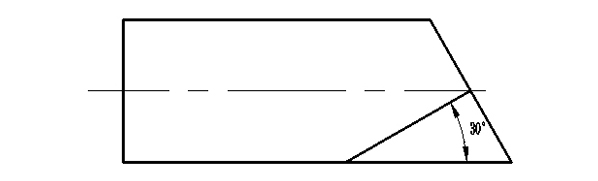
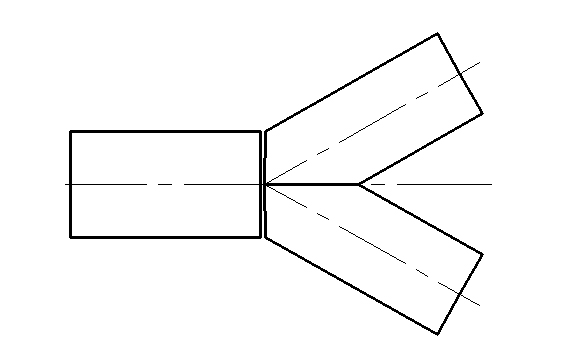
9.2 The procedure for tees producing
9.2.1 The materials are as the following diagram:
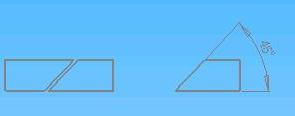
9.2.2 Welding as the diagram structure:
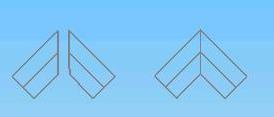
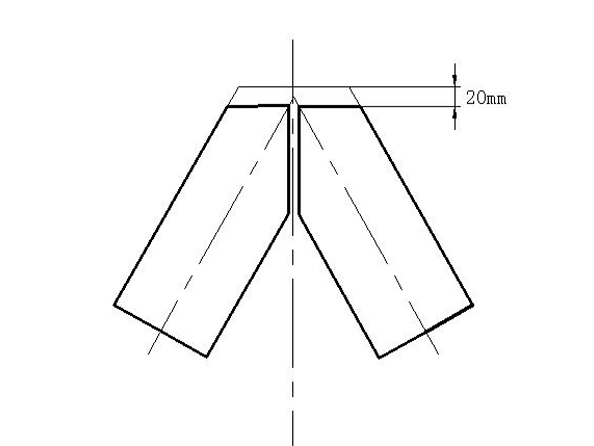
9.2.3 An angle is cut as the diagram
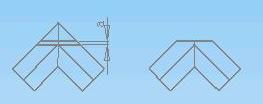
Notice: The dimension “a” should not be less than 20㎜which is as planning margin and compensating meltable bead.
9.2.4 Welding as the diagram structure, the tees have been produced.
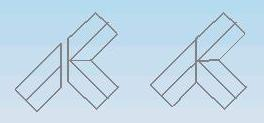
9.3 The procedure for the equal diameter cross pipes made
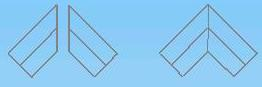
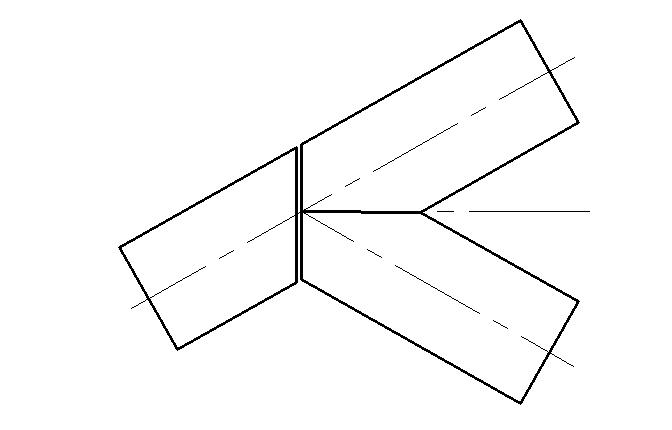
9.3.1 The materials are cut as the following diagram
9.3.2 The two couplers are welded as the diagram structure:
9.3.3 An angle is cut as the diagram:
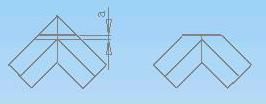
Notice: The dimension “a” should not be less than 20㎜,Which is planning margin and compensating meltable bead.
9.3.4 Welded as the diagram structure.
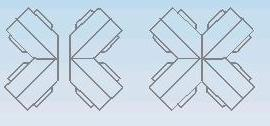
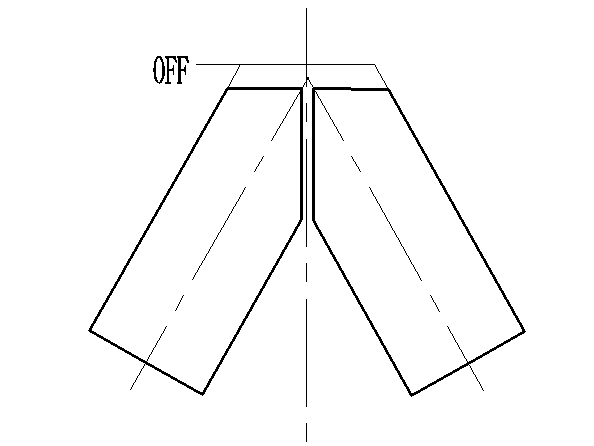
9.4 The procedure of “Y” shape fittings fabricating(45° or 60°)
9.4.1 cut as the following drawing(take 60°“Y” shape fittings as an example)
9.4.2 Proceed to the first welding as the following drawings:
9.4.3 Adjust the clamps and proceed to the second welding.
9.5 other fittings welding
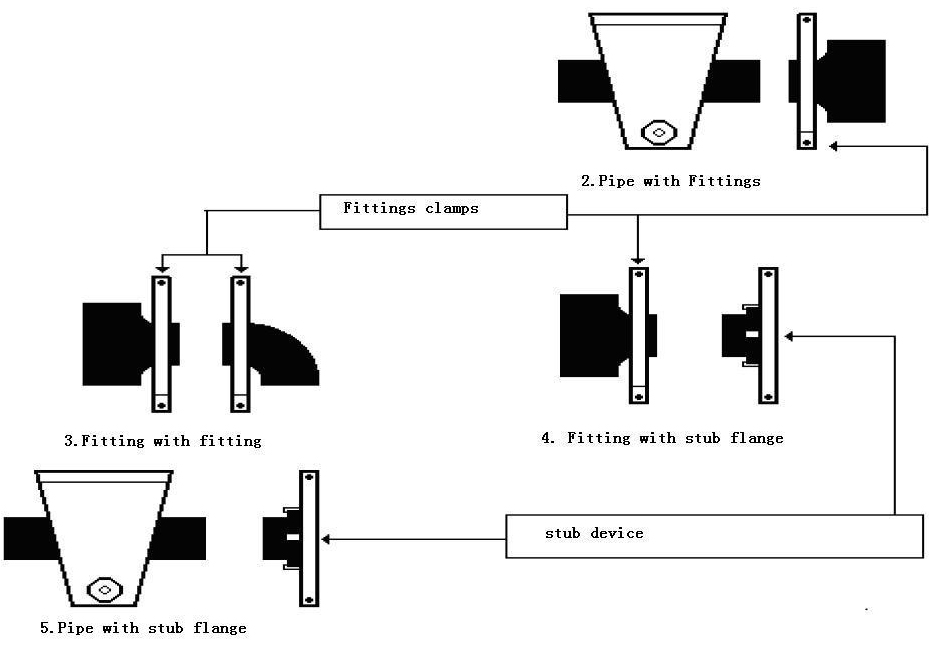
9.5.1. Pipe with pipe
9.5.2. Pipe with fitting
9.5.3 Fitting with fitting
9.5.4 Fitting with stub flange
9.5.5 Pipe with stub flange
Malfunctions Analyzing And Solutions
10.1 Frequent joints quality problems analyze:
10.2 Maintenance
u PTFE coated heating plate
Please take care on handling the heating mirror in order to avoid damages to the PTFE coating.
Keep always clean the PTFE coated surfaces, cleaning should be done with surface still warm by using a soft cloth or paper, avoiding abrasive materials in that might damage the PTFE coated surfaces.
At regular intervals, we suggest you:
- Clean the surfaces by using a quick evaporation detergent (alcohol)
- Check the tightening of the screws and the cable and plug condition
u Planing tool
It's strongly suggested to keep always clean the blades and wash the pulleys by using a detergent.
At regular intervals carry out a complete cleaning operation with an internal lubrication as well
u Hydraulic unit
The hydraulic unit does not need particular maintenance nevertheless the following instructions must be followed:
a. Check periodically the oil horizontal and in case add with oil type:
The horizontal should not be lower than 5 cm from the tank maximum horizontal.
A checking every 15 working days it's strongly suggested.
b. Replace totally the oil every 6 months or after 630 working hours.
c. Keep clean the hydraulic unit with particular care on the tank and quick couplings.
10.3 Frequent malfunction analyses and solution
During the using, hydraulic unit and electrical units may appear some problems. Frequent malfunction is listed as follows:
Please use tools attached, spare parts or other tools with a safety certificate while maintain or replace parts. Tools and spare parts without safety certificate are forbidden to be used.
|
Malfunctions of hydraulic unit |
|||||
|
No |
malfunction |
analyzes |
solutions |
||
|
1 |
The motor does not work |
is loosen
|
|||
|
2 |
The motor rotate too slowly with abnormality noise |
|
than 3 MPa
|
||
|
3 |
The cylinder works abnormally |
locked tightly
|
to outgo the air. | ||
|
4 |
Dragging plate moving cylinder does not work |
valve is blocked |
overflow valve (1.5 MPa is proper).
|
||
|
5 |
Cylinder leak |
1. The oil ring is fault2. The cylinder or piston isdamaged badly | 1. Replace the oil ring2. Replace the cylinder | ||
|
6 |
The pressure can not be increased or the fluctuation is too big |
1. The core of overflow valve is blocked.2. The pump is leak.3. The joint slack of pump isloosened or key groove is skid. | 1. Clean or replace the coreof over-flow valve2. Replace the oil pump3. Replace the joint slack | ||
|
7 |
Cutting pressure can not be adjusted |
1. The circuit is fault2. Electromagnetic coil is fault3. The overflow valve is blocked4. Cutting overflow valve is abnormal | 1. Check the circuit (the red diodein the electromagnetic coil shines)2. Replace the electromagnetic coil3. Clean the core of over-flow valve4. Check the cutting over-flow valve | ||
|
Malfunctions of electrical units |
|||||
|
8 |
The whole machine does not work |
|
1. Check the power cable2. Check the working power3. Open the ground fault interrupter | ||
|
9 |
Ground fault switch trips |
|
1. Check the power cables2. Check the electrical elements.3. Check the higher-up powersafety device | ||
|
10 |
Abnormally temperature increasing |
4. 4. Should the temperature controller readings be more than 300℃, which suggest he sensor may be damaged or the connection is loosen. Should the temperature controller indicate LL, which suggests the sensor have a short circuit. Should the temperature controller indicate HH, which suggests the circuit of sensor is open. 5. Correct the temperature by button located on the temperature controller.
|
contactors
controller
set the temperature
contactors if necessary |
||
|
11 |
Lose of control when heating |
The red light is shine, but the temperature still goes up, that is because the connector is fault or the joints 7 and 8 can not open when get the required temperature. |
Replace the temperature controller |
||
|
12 |
Planing tool does not rotate |
The limit switch is ineffective or the mechanical parts of planing tool are clipped. |
Replace the planning tool limit switch or minor sprocket |
||
Circuit & Hydraulic Unit Diagram
11.1 Circuit unit diagram (seen in appendix)
11.2 Hydraulic unit diagram (seen in appendix)
Space Occupation Chart